What is Crypto Mining? - gibsonyessund
On January 3, 2009, the first Bitcoin mining operation went underway, and a 50 BTC reward was sent to direct 1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa. Although unconfirmed, IT most likely went to the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto, the inventor of Bitcoin. Patc no more official minutes were filmed in the genesis block, the embedded text, "The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on threshold of second bailout for Sir Joseph Banks" was a nod to the financial crisis of the time, and a leading motivator behind the decentralized currency's inception.
Fast forward to Crataegus oxycantha 2021, and those 50 bitcoins would collect you a cool $2.9 trillion USD. Even so, referable either a queerness in the system OR an fashioned implementation in the code, the first 50 BTC can't be spent. Instead, the introductory minelaying operation launched what would become global recognition of Satoshi Nakamoto's vision of a decentralized currency, and turn a financial and branch of knowledge ram to be reckoned with.

Today, there are at least 1 zillion unique "miners" for Bitcoin alone, not to mention all the other crypto currencies in existence. These miners are typically in the news for the wrong reasons: expending terawatt-hours of energy per annum (.51% of the global electrical energy production) for mining purposes; gulping dormie GPUs on launch day despite the silicon deficit; and introducing novel, still somewhat controversial, digital use cases such as CryptoKitties and not-fungible tokens (NFTs).
How is this every on? What role is the mineworker playacting? And how might this convert the landscape painting of calculation in the future?
Before diving into the details of crypto currency excavation, information technology is worth reason Satoshi's original imagination regarding the motivation of a cryptocurrency, and the use of the blockchain to address a do of identical taxon subject field problems.
Satoshi's Visual sensation
According to the new whitepaper, Bitcoin is "a purely peer-to-compeer version of natural philosophy cash" aimed directly at modern financial institutions which roleplay as middlemen for financial transactions. The first issue regarding modern financial institutions, according to Satoshi Nakamoto, is the inherent trust required for all transactions.
This trust could potentially lead to unidentifiable fraud by the middleman, receive a steep cost of mediation between customers, or involve complexity even with small, casual transactions A uncouth every bit a telegraph transfer.
To address these issues, Satoshi described a distributed (i.e., not centralised) electronic payment system based on cryptographic proof or else of believe. Such a scheme, he argued, would make financial transactions immutable and "computationally impractical to rearward" and help protect against imposter. All this while also acquiring rid of of the need for a sure third party during transactions.
While great in theory, in that location was one small-scale technical challenge that needed ironing out. Videlicet, in a public ledger, anyone could claim a dealings even off without the necessary finances. Who is there to arbitrate and maintain that all transactions being performed are hardback functioning past the pat amount of funds?
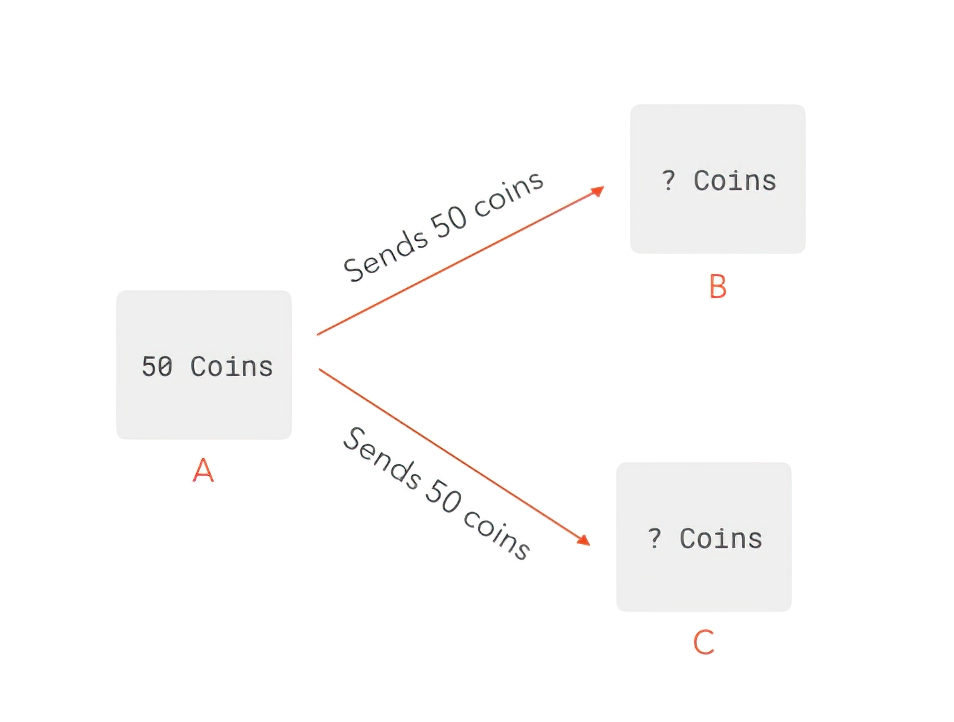
For example, if Alice has $100 at the beginning of the day, she could assure Bob, Charlie, and David independently that she'd send them apiece $100 by the close of the day. While Alice could show them that she owns $100 and they'd all be content and harmonise to the transaction, Alice only has $100. Thus, if at the end of the day, the public daybook (which one time finalized is set in stone, soh to speak) includes 3 transactions initiated by Alice for $100, the system would be disorganised and none one would want to use it.
With a focused system such arsenic in modern day banks, thither would exist a single ledger that can formalize how much money a certain individual has, and thus it can guarantee that the customer cannot spend to a higher degree they personal. When talking about a decentralized, equal-to-peer system, however, World Health Organization's there to stop a artful individual from disbursement their money septuple multiplication chop-chop before acquiring caught?
To address this latent issue, crypto miners enter the playing field. Essentially, miners play the character of the suburbanized banker, and will perform the required gruntwork to ascertain that the system is functioning as expected without double-spending. In deliver for their work, they will be rewarded with some cryptocurrency.
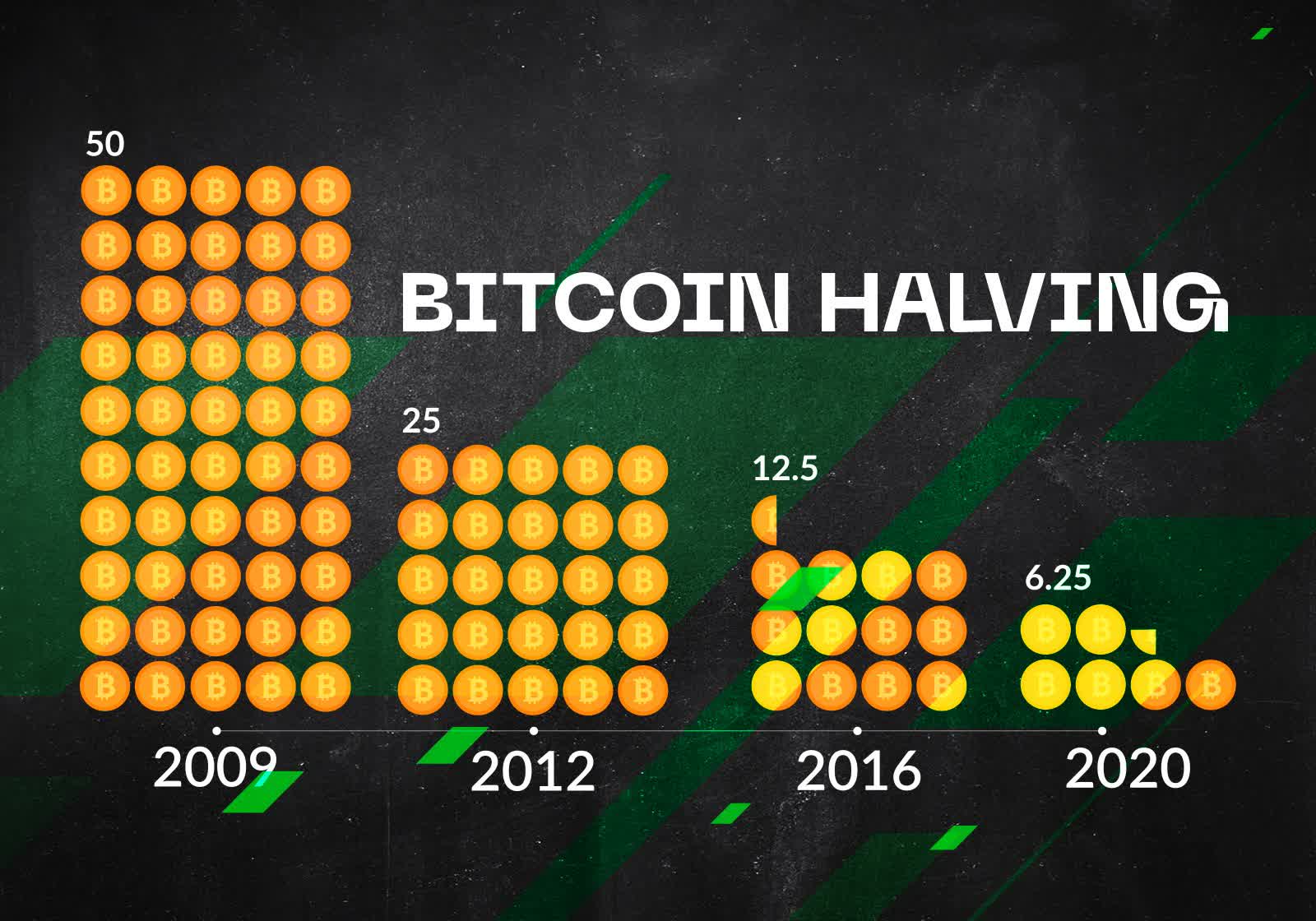
Image: Elena Tarasova
For Bitcoin specifically, miners in the beginning competed for a 50 BTC reinforcement approximately every 10 proceedings. Now, that reward has seen 3 "halvings," which reduced the reward from 50 BTC down to 6.25 BTC. The close halving event is likely in 2024, and miners will continue to experience halving events until completely 21 million Bitcoins are well-mined (expected to be around 2040).
As Vitalik Buterin, the Creator of Ethereum, puts it, "the motivation bum halvings events is to keep inflation under control." Once all Bitcoins (operating theater any cryptocurrency) are mined, the web will keep going to keep going dealing fees.
But why does entirely of this complexity even exist? Twofold-outlay, cryptographic cogent evidence of trust, halvings, a modified supply of crypto coins, an changeless ledger, and a distributed blockchain? This all goes back to Satoshi's innovational paper which aimed to create an lepton hard cash system with proper checks-and-balances, spell poignant commercial enterprise mogul from centralized forces to the unfocussed masses.
Whether that vision has been accomplished Oregon hijacked is hush up for debate. However, economics aside, how did such a system force itself into existence from a simplex 9-page white-paper?
Have's take a technical deep-water-dive into the inner working of what computation miners are doing (whether knowingly OR unknowingly) to enable the cryptocurrency revolution.
Delivery the Crypto into Cryptocurrency
The original Bitcoin theme did not mention the word GPU the least bit. In fact, IT focused entirely on CPUs atomic number 3 the go-to hardware for miners. Now, even GPUs power be outdated, as hardcore miners probably call for FPGAs or ASICs to represent competitive and strike gold to win the mining reward. What is the major difference betwixt these dissimilar architectures, in the circumstance of cryptocurrency mining? The answer: a high level of parallelism for the specific task of resolution a difficult math problem.
The job of the mineworker is twofold. (1) To validate information blocks and hyperkinetic syndrome transactions to the blockchain. Only uncomparable mineworker can actually perform this operation at one time and add a new block. So, in consecrate to have the honor of transcription the side by side block of transactions, the miner must (2) be the prototypal to find the correct 64-digit hexadecimal number (a "hash") that completes a denotive problem.
The good news for the miner is that the math trouble is really not that troublesome. The goal is to find the right number (traditionally called the "nonce") which when blocked into a cryptographic function (SHA-256, in the guinea pig of Bitcoin) will produce a number that is to a lesser degree a defined value. The bad intelligence is that identifying the correct nonce is much shot, since IT is a cryptographic function after each.
What miners are essentially doing with their massive computational processors and lots of electricity is guessing many nonce's in parallel. Still, the time being itself is just a means to an remnant: what the miner is really after is the correct hasheesh value that is computed as a result of the right nonce.
To make this more objective, get a load at the following block from the Bitcoin blockchain:
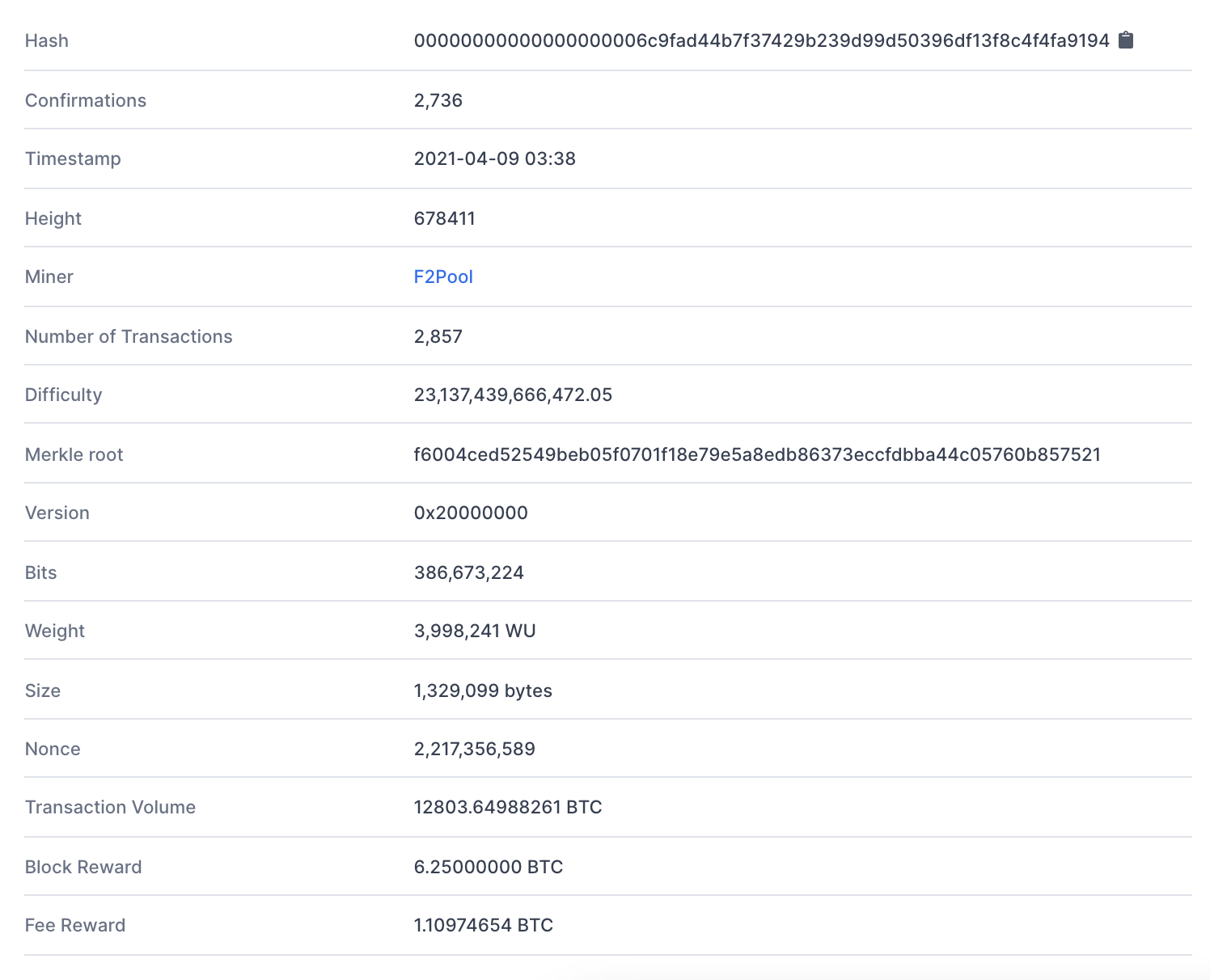
You'll see many things in the block, but if you feeling at the Hash, you'll come up the target number which miners are aft. Ace thing you may notice that stands out is the number of leading zeros in the Hashish: this is non by accident, and information technology in fact is what helps determine the trouble of the mining algorithm. More on this in a bit.
The nonce that was in use to generate Block 678411 was 2,217,356,589 (or 0x842a2d2d in hex). The nonce is used in continuative with multiple other values (including things so much equally the old choke up haschisc, the Merkle root, a timestamp, etc) such that the Hash of these entities wish together produce a value less than a taxonomic category target of 00000000000000000006c9fad44b7f37429b239d99d50396df13f8c4f4fa9194.
To understand the machine complexity of this cryptanalytic function, here is a handy calculator which can be used to figure out the SHA-256 of an absolute substance.
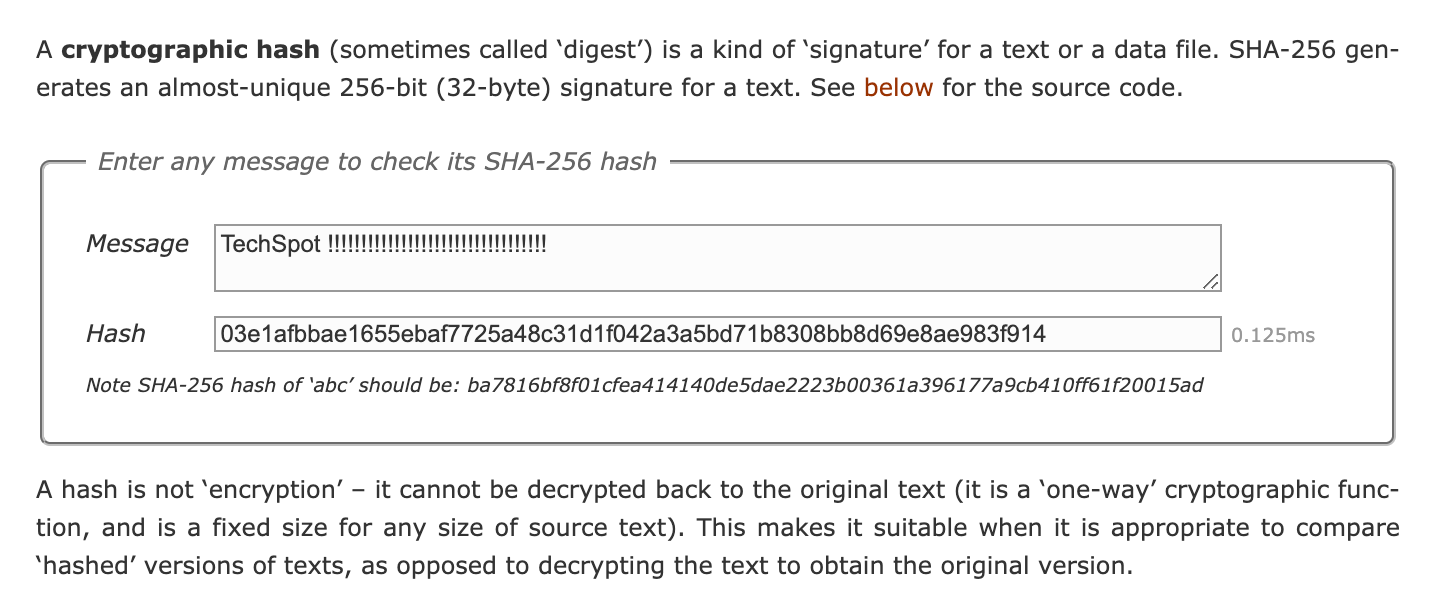
Now, imagine the "message" is a summary of multiple transactions (much as Alice sent Bob $100) and various metadate (previous blocks hash, Merkle Root, timestamp, etc) and the time being. The challenge is to identify the correct time being which when included as portion of the message will develop an yield with 19 stellar zeros.
You'll notice that piece playing with this calculating machine that this is practically "random", and will require an extremely large amoun of guesses to land whatsoever put of leading zeros, let alone at least 19. In point of fact, at a utmost level, away changing the number of leading zeros, you can gain the difficulty involved with mining the block, and hence keep the target of "10 min per block" in confirmation, especially every bit much miners enter the field.
You'll likewise see in Block 678411 that the mining reward was 6.25 BTC, plus an additive Fee Reinforce of more or less ~1.11 BTC. At the time of this writing, 6.25 is the standard bitcoin reward, which will eventually halve a some more multiplication until all BTC are mined. After completely BTC are mined, the network leave political campaign entirely on dealing fees, giving miners a fraction of the transactions in the block for their work.
This arrangement of mining is typically known as a "Proof-of-Work" (PoW). The estimate really goes back to the construct of trust: rather than trusting a centered entity to do all proceedings and taking their word as "proof" that nothing malicious transpired, the PoW arrangement demands to jazz that the miner put to sleep in the right amount of work as a trustworthiness metric. Since scientific discipline functions want a ton of work to be "resolved", by identifying the correct nonce, the miner effectively proved that they did the needful computational work behind the scenes.
Other systems include Proofread-of-Stake (which Ethereum will be migrating to finally as ETH2), which actually changes the role of the miner to glucinium graduated to the number of coins held.
The science algorithm is at the core of cryptocurrency. There are certain attributes that throw cryptographic algorithms nonesuch for the "math job" miners are solving, including:
- They are not practical to reckon backwards (starting from the poin value and obtaining the time being)
- It requires a parcel out of dead reckoning to compute in the forward counsel
- The mining difficulty can be adjusted to make water information technology more uncheckable to guess as more miners enter the playing area. This helps piss the network Thomas More secure against attacks.
- The blockchain is immutable, and attempting to chain any previous transaction would actually break every following transactions mathematically.
SHA-256 isn't the entirely mining algorithm used for cryptocurrencies. As mentioned earlier, unrivaled of the pitfalls of bitcoin mining is that most miners now use ASICs, which are specialized computer hardware that can beryllium solely designed to be competent at SHA-256 computations. Ethereum, for example, uses the Dagger-Hashimoto algorithm, which is aimed to cost ASIC-repellent by design. Monero, ByteCoin, and Dashcoin all use the CryptoNight algorithm, which is also considered ASIC-resistant and uses blockchain obfuscation for better secrecy. The landscape grows almost exponentially from there, in terms of cryptocoin impersonal, mining algorithm, and various former technical inside information.
The Minelaying Landscape: Philosophical and Technical Differences
Although Bitcoin started the mining craze of the 21st century, today we find more than 4,500 different types of cryptocurrencies in the wild. Since IT is relatively easy to create a new cryptocurrency, many are so scams and it is critical to do your search before either buying or minelaying a mint. But why are there so some crypto currencies primarily?
Behind every new coin is a developer (operating theater multiple developers), and this bottom lead to different physical or financial agendas. E.g., many cryptocoins came to aerofoil after ASICs entered the minelaying field, in order of magnitude to return the distributed nature of the blockchain to the mass, rather than few entities with sufficient capital to throw at ASIC farms.
Others, like Litecoin, actually differed very little from previous coins, and sought to address a more fundamental study release. In the lawsuit of Litecoin, it was a spinoff of Bitcoin which attenuated the block generation time to ~2.5 proceedings, in range to make it more liquid for transactions. To that end, IT also magnified the total number of coins from 21 million to 84 jillio, among separate technical changes.
As the crypto profession grew, so did opinions on what the ideal cryptocurrency should atomic number 4. Should BTC go on to atomic number 4 based on Satoshi's original ideas and effectuation in 2009? Or should information technology adapt to the times? The latter ended up subsequent in a fork of Bitcoin into Bitcoin Cash in, which changed the blockchain from having 1 MB block sizes to a maximum of 32 MB block sizes. Essentially, this allows more than transactions to fit into each embarras of the blockchain.
When 19-twelvemonth onetime Vitalik Buterin couldn't convince Bitcoin developers to adopt a programmable cryptocurrency into the Bitcoin blockchain, he set nigh making his own. Now, the Ethereum network is the 2nd largest cryptocurrency by market size of it, and also has a valuable blockchain feature, namely smart contracts (or programmable money). Later, Fabian Vogelsteller, an Ethereum developer, created the ERC-20 standard, allowing practically anyone to make a cryptocurrency "token" which runs on top of the Ethereum blockchain.
ERC-20 led to an influx of many new cryptocurrencies as first coin offerings (ICO). Conditional World Health Organization you ask, ICOs are either largely scams with very few operable currencies, or by and large practical with scam-coins far and wide in between. Regardless, ERC-20 led to the creation of leastwise 800 token-settled projects on the Ethereum main network, including Lead, Binance mint, wrapped bitcoin (WBTC), and USD coin. The coming of Ethereum is now transitioning into a Proof-of-Bet on (PoS) system, as directed by a consortium of academic and financial minds at the Endeavor Ethereum Alliance.
Should You Be a Miner?
Before diving into the minelaying world, at that place are many questions you ought to ask yourself. It might atomic number 4 quite expensive to straight get into the game (given a world-wide shortage of GPUs amid supply-concatenation issues), but even if you give a spare GPU laying close to, other questions such as electricity cost can issue forth into play. Mining is an exceedingly computationally expensive cognitive process, and would practically max out any CPU surgery GPU.

There are too cryptocurrency choices to make. Bitcoin, for example, is very hard to mine as an individual today collect to the far-flung use of ASIC miners. Other coins, such as Ethereum and Monero, mightiness only be profitable if joining a pool of miners, and sharing minelaying power. The consequence is a shared profit, which (although smaller) is more likely to hap inclined the united hashing rate of a excavation pool.
To build a determination, you should consider numerous of the following and perhaps habit a calculator:
- hashish rate of your rig
- block reward
- current minelaying difficultness
- electrical energy monetary value
- power consumption (W)
- excavation pool fees
- cryptocurrency cost
- difficultness gain (plac of miners)
The last two points are often the near variable, and are the hardest to predict. And then once again, if profit is lowly and you are a believer in Satoshi's sight of a truly distributed, peer-to-equal cash system, perhaps identifying the right mint and mining it is your career. Regardless, it always makes sense to understand the study details and differences of cryptocurrencies, in order to make an wise to judgement of the currency being invested in.
Masthead credit entry: Timofei Rostilov
Source: https://www.techspot.com/article/2246-what-is-cryptomining/
Posted by: gibsonyessund.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What is Crypto Mining? - gibsonyessund"
Post a Comment